The causes of papillomas on the body surface in women are in most cases related to the infection of the body with the papillomatosis virus. There are also congenital formations that are transmitted along with genetic information from one of the parents.
What is a papilloma
Papillomas are benign neoplasms on a woman's body caused by the pathogenic activity of viral microorganisms of the papillomavirus family. Translated from Latin, "papillo - nipple" and "oma - a typical endpoint for all types of tumors".
Papillomas are formed from the host's own epithelial cells. Externally, it looks like a connecting papilla with a flat, sharp, rounded or branched shape.
A distinctive feature of this type of benign neoplasm is that it is able to develop on the oral mucosa, internal organs with a hollow structure, inside the nasal cavity, in the paranasal sinuses, on the vocal cords.
Initially, the root of the papilloma is formed from a flat epithelium with a gradual growth above the general skin.
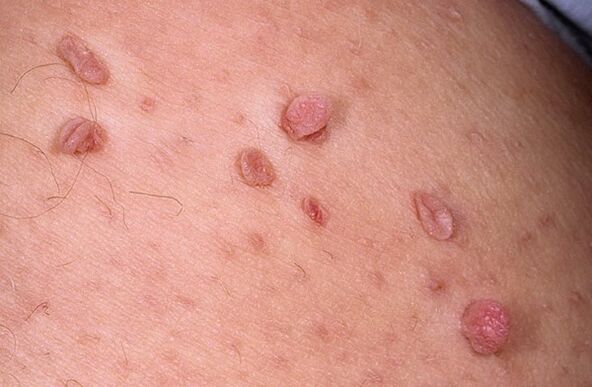
The color of the tumor can range from flesh to brown and pink. . . Localization of papillomas in the bladder, intestines, organs of the respiratory system can lead to the simultaneous development of diseases and complications.
Types of papillomas on the body of women
Depending on the location of the warts, their appearance and the reasons for their formation, different types of papillomas are distinguished. The table below lists the types of these types of benign neoplasms, indicating their characteristics.
| Type of papilloma | Characterization of neoplasm |
|---|---|
| Genital warts | They can be found in any part of a woman's body. Externally, they look like an elongated suspended pier, which in most cases has a brown tinge. |
| Papilloma vulgaris | Form of classical human papillomatosis virus. Neoplasms are round in shape, attached to the main surface of the body on a thin and short stalk. It is flesh-colored, just like the rest of the dermis. |
| Genital warts | Localization of this type of neoplasm is an intimate area for men and women. The infection results from unprotected sex with an infected partner. The main location of tumors is the circumference of the anus, labia majora and minora for women, foreskin for men. Non-compliance with sanitary and hygiene standards can lead to household contamination. |
| Senile warts | Found in older women. They appear as a result of hormonal changes in the body, metabolic disorders, prolonged exposure to open sunlight. The main danger of this type of papilloma is the high risk of its degeneration in malignancies. |
| Plantar | This type of papilloma is localized only in the plantar part of the foot. Externally, they resemble the head of a small cauliflower with branched inflorescences. If a woman walks a lot, wears tight shoes, plantar warts can become inflamed, bleed and cause pain. |
Almost all of the above types of papillomas are caused by a woman becoming infected with one or the other genotype of the human papillomavirus. The only exceptions are senile warts, which can appear due to age-related changes in the body of the elderly.
Stages and grades of papillomas on the body of women
Like any other benign tumor, the papilloma on a woman's body develops in several stages.
In this regard, the following stages of wart formation are distinguished:
- Stage 1- uncontrolled breakdown of squamous cell epithelium and formation of papilloma root, which is asymptomatic and imperceptible;
- Stage 2- the formation of a wart head that rises 1 to 1. 5 mm above the general surface of the body, if it is at the folds of the joints, in the lumbar region, on the neck or under the armpits, can cause discomfort, friction, skin irritation;
- Stage 3- a full-fledged flat, rounded or elongated neoplasm with a root, a leg, a main body in the shape of a head and a blood supply due to the smaller capillary vessels connected to the other epithelial tissues appear;
- Stage 4- multiple proliferation of similar papillomas resulting from the division of existing neoplastic cells (extensive papillomatosis is dangerous with a high probability of malignant degeneration of one wart).
The stage of the skin disease is determined by the dermatologist during the patient's examination. The method of treatment is chosen based on the results of the diagnosis, the type of papilloma and its stage of development.
Papilloma symptoms
Papillomas on the body (the causes in women that cause neoplasms are related to a viral infection) are individual or multiple benign tumors that are easy to detect by external signs.
The symptoms of female papillomatosis are as follows:
- the appearance of a small tubercle rising above the general surface of the epithelium;
- wart root enlargement, which becomes larger every week;
- a foreign neoplasm with a round, branched or conical shape appears on the body;
- the main sites of papilloma on the woman's body are the armpits, the inside of the thighs, the neck, the surface of the skin under the mammary glands, the groin area, the perineum, the genitals, the back, the plantar part of the legs;
- prolonged exposure to the wart surface may cause friction and pain;
- papilloma may have a flesh, yellowish, pink, brown hues, which is the norm;
- Attempts to remove the neoplasm itself do not lead to a positive result, and the cut wart grows again.
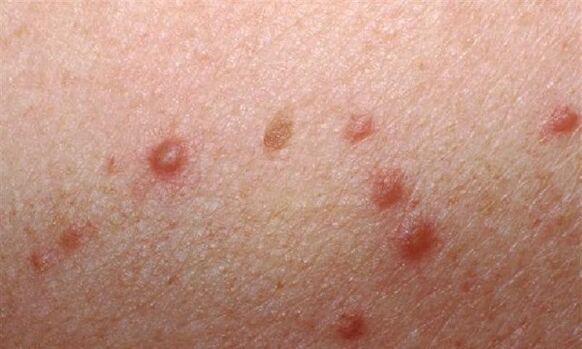
The presence of symptoms such as a sudden discolouration of the warts to darker colors, the onset of an acute inflammatory process, the discharge of pus or blood fluid, and pain attacks are alarming signs that are not typical of papillomatosis. In this case, degeneration of the benign formation in the cancer is not ruled out.
Reasons for consideration
Papillomas on the body (causes in women who provoked the disease may be related to the patient's lifestyle) are chronic dermatological pathologies that appear under the influence of such factors.
Papilloma factors on the body:
- to lead a sex life, to have close contact with an infected partner without using barrier contraception;
- sharing towels, cosmetics, soap and other hygiene products with a person suffering from the papilloma virus;
- shared slippers and other footwear;
- visiting public showers, baths, swimming pools, open-air steam baths that touch surfaces where viable papillomavirus virions are located;
- hormonal imbalances in the body caused by concomitant diseases of the endocrine system;
- getting a viral infection into an open wound during shaving;
- infection of a child from a fetal mother during the transition through the birth canal.
In most cases, it is not possible to determine the true cause of the warts on the body. The incubation period for papillomavirus after infection is from several days to 3 or more years.
Diagnostics
In order to make an accurate diagnosis in the form of papillomatosis, a woman must undergo a comprehensive examination of the body and directly of the skin area where the benign tumor is located.
Diagnosis of papillomas takes place in several stages, namely:
- visual inspection by a dermatologist;
- donation of venous blood for its biochemical study and detection of papillomavirus virions;
- examination of deeper epithelial layers of warts using a dermatoscope;
- capillary blood collection for clinical analysis;
- selection of a papilloma particle for further histological examination to exclude the oncological nature of the tumor origin;
- morning urine delivery to determine its biochemical composition and overall female health.
Additional gynecological examinations and tests for sexually transmitted infections may be required to localize papillomas in the intimate area, on the genitals and around the anus.
When to see a doctor
The main dangers of this type of warts are aesthetic defect, as well as the risk of their degeneration in oncology.
It is recommended to consult a dermatologist as soon as a foreign neoplasm is detected.
Early diagnosis and detection of papilloma allow effective treatment and removal of the neoplasm with minimal risk of complications.
Papilloma prevention on the body
Papillomas on the body (the causes of warts in women can be prevented by effective prevention measures) are benign tumors that can be easily prevented by following these rules.
For instance:
- lead an orderly intimate life, be only one sexual partner;
- wear only your shoes and do not let others wear them;
- use barrier contraception;
- avoid visiting public baths, toilets, swimming pools, showers, as well as do not put your feet in rubber slippers, do not touch open body parts on wall surfaces, door handles, tiles, sun loungers;
- use only your cosmetics, towels, soap;
- undergo a preventive medical examination by a dermatologist at least once a year;
- balance your diet, sleep at least 8 hours a day, get enough rest to ensure the normal functioning of the immune system.
All of the above recommendations do not guarantee 100% protection against papillomatosis infection, but they do reduce the risk of the disease and avoid contact with possible sources of infection.
Methods of treating papillomas on the body of women
Papillomatosis is a completely incurable disease. A woman infected with the virus that causes warts will wear it for the rest of her life. Modern methods of treating the disease can get rid of the consequences of the pathology in the form of benign neoplasms.
Medicines
Traditional medicines do not completely get rid of papilloma, as these types of warts have to be removed by chemical, thermal, electrocoagulation, laser or surgical treatment.
Traditional methods
Alternative medicine offers its own alternative ways to get rid of papillomas, regardless of their type and location on a woman's body. The following are traditional wart removal methods.
Knitting with thread
You have to wait until the moon phase is declining. You will need to take a piece of black thread, use it to tie the papillomas by tying a knot. This thread is taken out in the garden and buried in the soil with the words, "When this thread collapses, all my warts will disappear. " After 2-3 weeks, the papilloma will begin to soften and collapse without signs of pain or inflammation.
Special features
Warts and papillomas are special remedies, but they do not work and guarantee relapse. One of these tools is, for example, a special patch.
Such products usually contain natural ingredients that neutralize the virus to some extent.
Dog saliva
To get rid of benign neoplasms using this method, you need to spread the wart with an even layer of sour cream. The woman should then go to the dog to lick the lactic acid product with her tongue.
The papilloma is then sealed with a medical adhesive plaster. Saliva cannot be wiped off the neoplasm. After 1 week, the patch can be removed. From now on, the wart will start to crumble.
Moxibustion with celandine
During the growing season of this plant (from late May to mid-June) every day should be plucked celandine branches and warts cauterized with poisonous yellow juice. The duration of therapy is from 10 to 30 days. Precautions should be taken to prevent juice from entering the mucous membranes of the mouth and eyes.
The effectiveness of the above folk remedies for removing papillomas from the body has not been proven by official science. Women who used similar recipes were able to achieve the desired result and respond positively to these therapies.
Other methods
The most effective way to treat papillomas is to remove them completely.
The following methods are used for this purpose:
- chemical incineration- provides action on the surface of the wart with aggressive solutions based on acids, potassium or sodium hydroxide;
- electrocoagulation- the papilloma is cut off and cauterized using a loop-shaped instrument, the metal end of which is under electric current (the treatment procedure is performed under local anesthesia);
- cryodestruction- the benign tumor is burned using liquid nitrogen solution (under the influence of low temperature, the epithelial tissue freezes and then breaks down into parts);
- laser coagulation- papilloma excision is performed using positively charged laser particles, removal of the main body of the wart and cauterization of its root system is ensured;
- surgical removal- the traditional and most common method of treating dermatological disease, which consists of cutting the wart with a scalpel and then applying suture material.
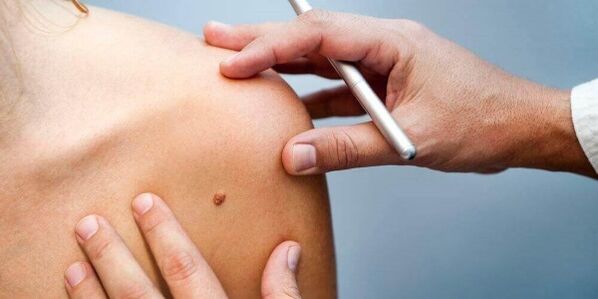
All of the above treatments for papillomatosis allow the removal of benign neoplasms with minimal risk of recurrence.
The average rehabilitation period is from 3 to 7 days. The safest method is laser cutting and electrocoagulation. The most painful and traumatic treatment is traditional wart surgery.
Possible complications
In the absence of adequate responses and treatment of papillomatosis on the body, a woman may experience such complications over time.
Possible complications:
- the appearance of similar warts on other parts of the body, indicating an increase in viral activity;
- wart degeneration in a cancer that can cause death;
- the appearance of similar neoplasms in the bladder, intestines, larynx, trachea, which will lead to their dysfunction, urinary, respiratory and digestive disorders;
- cervical cancer (scientific studies show that 80% of women suffering from the disease are infected with the human papillomavirus;
- increase in wart size, creation of a cosmetic and aesthetic defect;
- neoplasm injury and bacterial infection entering epithelial tissues.
To prevent papillomas from appearing in women, it is important to remember the causes. This will maintain the health of the skin and prevent a decrease in the immune status of the pathogenic activity of the papillomavirus. The disease itself is not life-threatening, but its presence can lead to the development of severe complications.
















































































